

DCIS is very treatable and highly curable – but in some cases, if left untreated, it has the potential to become invasive breast cancer. In DCIS, the cancerous cells are in the breast’s milk ducts. In some cases, calcifications on a mammogram represent the earliest form of breast cancer, which is called ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). If the calcifications are confirmed to be benign, which is most often the case, the patient can then return to their regularly scheduled mammograms.
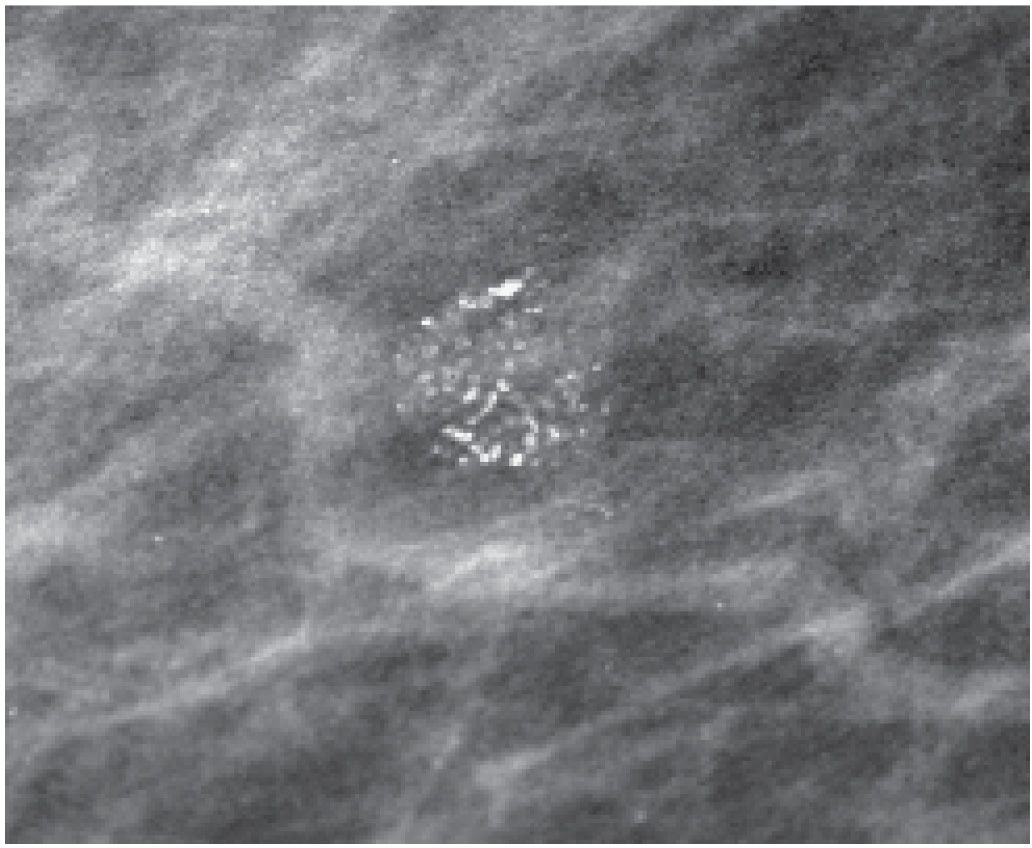
Most of the time, the biopsy will show that the calcification is not cancer. If deemed necessary, a biopsy will be recommended to check for underlying cancer. The follow-up mammogram is used to take a closer look at the concerning calcifications to better determine if they are benign or in need of further testing. If the calcifications are tightly clumped together, look different from one another, or have a linear appearance, a radiologist may recommend a follow-up mammogram or a biopsy. When they appear to be scattered and similar in appearance, they are usually benign (or harmless) and a biopsy or further testing is not needed. They cannot develop into cancer rather, calcifications can be an indicator of some underlying process that involves the cancerous cells.ĭuring a mammogram, calcifications appear as small white dots in the breast tissue. What is the relationship between breast calcifications and cancer?Īs breast tissue ages and changes naturally, calcifications can be a normal byproduct of those changing cells. They can only be found using mammography or, rarely, ultrasounds. There are a variety of causes for calcifications, including:Ĭalcifications, unlike lumps, cannot be detected using touch. How are breast calcifications detected?Ĭalcifications are a common find on a mammogram, with increasing prevalence after the age of 50. On rare occasions, however, calcifications can be an early marker of breast cancer. Breast calcifications, or small calcium deposits in breast tissue, are signs of cellular turnover – essentially, dead cells – that can be visualized on a mammogram or observed in a breast biopsy.Ĭalcifications are generally harmless and are often a result of aging breast tissue. What are breast calcifications?Īll cells in the body have a life span the cells that line the milk ducts of the breast only live for so long. In rare instances, they can be an early sign of breast cancer, though calcifications themselves do not develop into cancer. Receiving the news that something abnormal has turned up on a routine mammogram can be frightening, but breast calcifications are usually harmless.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
